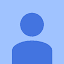
Retaining walls are an essential feature in many landscapes, providing both functional and aesthetic benefits. As the name suggests, a retaining wall is a solid and sturdy structure designed to retain materials such as soil, preventing erosion and landslides. These walls help counteract the natural pressures that soil exerts when situated on slopes, making them critical additions to properties in hilly or sloped areas.
While retaining walls are commonly used for soil stabilization, they can also be incorporated into landscaping projects to create terraced gardens, raised sections, and visually striking outdoor spaces. If you are considering adding a retaining wall to your property, there are several key factors to understand before hiring a professional contractor.
Types of Retaining Walls
Retaining walls come in different types, each suited to specific terrains, structural requirements, and property layouts. Before starting construction, it is important to familiarize yourself with the different types of retaining walls available.
Gravity Walls
As the name implies, gravity retaining walls rely on their weight to hold soil in place. These walls are typically built from heavy materials like stone, concrete, or bricks, providing a strong and dependable barrier against soil movement. They are often used in hillside properties where significant reinforcement is needed.
- Best suited for residential yards, garden beds, and steep slopes
- Common materials used include stone, concrete blocks, and poured concrete
- Strong, durable, and low maintenance
Sheet Pile Walls
Sheet pile walls are a cost-effective and simple solution for areas with soft or loose soils. These walls are constructed by inserting vinyl, steel, or wood planks deep into the ground, where the sheer force of the embedded portion holds back the soil.
- Best suited for narrow spaces, waterfront properties, and unstable soils
- Common materials used include steel, vinyl, and wood
- Strong and ideal for water-adjacent applications
Anchored Retaining Walls
 The anchored retaining wall style adds extra reinforcement using steel cables or supports that are driven deep into the ground behind the wall. This additional anchoring helps withstand high lateral pressure, making it an ideal choice for very tall or high-load retaining walls.
The anchored retaining wall style adds extra reinforcement using steel cables or supports that are driven deep into the ground behind the wall. This additional anchoring helps withstand high lateral pressure, making it an ideal choice for very tall or high-load retaining walls.
- Best suited for large-scale retaining projects, commercial properties, and highways
- Common materials used include reinforced concrete and steel cables
- Designed for high-strength support on steep slopes
Brick and Timber Walls
For homeowners looking for aesthetic charm along with function, brick or timber walls offer a classic and stylish look. Though not as durable as stone or concrete walls, these materials work well for decorative, low-height landscaping walls.
- Best suited for garden landscaping, flower beds, and minor erosion control
- Common materials used include pressure-treated timber, bricks, and decorative stones
- Enhance curb appeal while serving a functional role
Uses of Retaining Walls
Retaining walls have a variety of applications, not just for hillside protection but also for enhancing properties. They can be used to:
- Prevent soil erosion and protect the structural integrity of a property
- Support roads, bridges, and commercial properties
- Create terraced landscaping and distinct outdoor spaces
- Strengthen coastal shorelines and flood-prone areas
For homeowners, retaining walls can provide additional lawn space, organize outdoor areas, and add to the overall aesthetic value of the property.
Choosing the Right Materials for Your Retaining Wall
The materials used for retaining walls depend on the purpose of the wall, associated costs, and the desired appearance. Some common options include:
- Concrete – A durable, long-lasting material that can be shaped, textured, and colored to match different outdoor aesthetics.
- Stone – A natural and highly durable material that offers a classic look. While more expensive, stone walls require minimal maintenance.
- Brick – A strong and visually appealing material that complements traditional homes and gardens. Bricks retain their structure well and require occasional maintenance.
- Wood and Timber – A budget-friendly and easy-to-install option, but prone to decay in wet climates unless properly treated.
The right material will depend on budget, structural requirements, and the specific design envisaged for the landscape.
Retaining Wall Costs and Budget Considerations
The costs of retaining wall installation vary based on factors such as:
- The height and width of the retaining wall
- Choice of materials, with stone or concrete typically costing more
- Labor costs for excavation, reinforcement, and finishing
- Site preparation, including grading and drainage solutions
- Permit requirements based on local regulations
For those looking to minimize expenses, lightweight retaining walls using timber or decorative bricks may be suitable for smaller projects, while reinforced stone or concrete remains the best option for long-term durability.
Drainage Considerations for Retaining Walls
Drainage management is essential for ensuring the longevity of a retaining wall. Without proper water redirection, accumulated water can weaken structural integrity, causing cracks and eventual collapse.
Some effective drainage strategies include:
- Installing perforated pipes behind the wall to allow water to escape
- Using gravel backfill to improve water drainage and reduce hydrostatic pressure
- Integrating weep holes for controlled water drainage through the wall
Checking for nearby water sources, such as ponds or runoff risks, that may require adjustments in wall placement or additional waterproofing measures
Do You Need a Permit for a Retaining Wall?
Permit requirements vary by location, but in general:
- Walls under 12 inches may not require permits
- Walls over four feet often need residential building permits
- Commercial walls over six feet may require engineering reviews for safety codes
Checking zoning regulations in advance is recommended to avoid project disruptions or legal complications.
Why Hire a Professional Retaining Wall Contractor?
Installing a retaining wall is a strategic project requiring proper engineering. Hiring a contractor ensures that:
- The right construction materials and reinforcements are used
- The wall is built with appropriate drainage considerations
- Errors and future structural problems are avoided
- The finished structure meets zoning and safety regulations
Attempting a DIY retaining wall may result in significant repair costs if the structure fails due to improper engineering or lack of reinforcement.
Work with Experts for Your Retaining Wall Needs
 Are you considering a retaining wall for erosion control, landscaping design, or structural support? Dirt Connections provides high-quality retaining wall solutions tailored to residential and commercial needs.
Are you considering a retaining wall for erosion control, landscaping design, or structural support? Dirt Connections provides high-quality retaining wall solutions tailored to residential and commercial needs.
- Experienced professionals to assess your property
- Custom material recommendations for durability and style
- Precision-built retaining walls designed for longevity
Contact Dirt Connections today to schedule a consultation and take the first step toward a durable and beautifully designed retaining wall.